Explore the importance of carbon intensity in reducing environmental impact and transitioning to cleaner energy solutions.
Carbon (CO2) intensity is a metric that has grown increasingly important in our global conversation about climate change and environmental sustainability. Carbon emissions refer to the total amount of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere from various sources, while carbon intensity measures the emissions per unit of energy or economic output. Measuring carbon intensity allows us to compare the environmental impact of different energy sources and understand which are cleaner, or have a lower carbon footprint, and which are more harmful to the planet. By creating an ‘apples to apples’ comparison across different energy types, carbon intensity provides a standardized metric that helps to put all energy sources on an even playing field, making it easier to evaluate and prioritize cleaner energy solutions based on their true environmental costs.
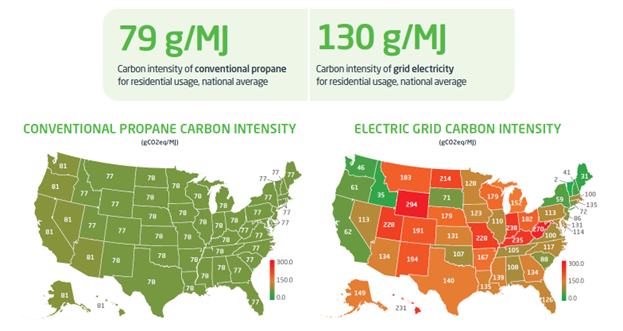
The calculation of CO2 intensity for propane involves tallying the carbon dioxide emissions from its production, transportation, storage, and burning. Similarly, for electricity, it encompasses emissions from resource extraction (like coal or natural gas, and materials for solar panels and wind turbines), electricity generation, and the transmission, distribution, and usage of the electricity. The measurements are generally given in kilograms per million BTU (kg/mmBTU) or grams per Megajoule. This comprehensive measurement of emissions from ‘cradle to grave’ ensures that all environmental impacts associated with the lifecycle of the energy source are considered, providing a full spectrum of emissions data.
Why is Carbon intensity crucial?
It plays a significant role in our efforts to combat climate change.
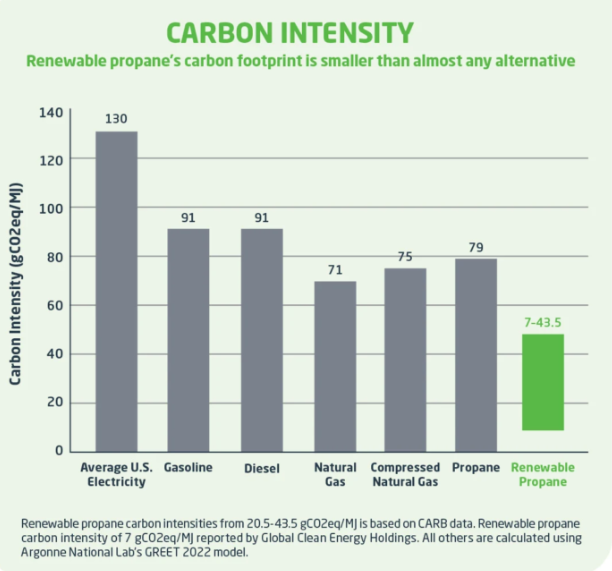
By understanding the carbon intensity of various energy sources, governments, businesses, and individuals can make informed decisions about energy consumption and production. For example, energy derived from sources like propane, wind, solar, and hydro typically has a much lower carbon intensity compared to fossil fuels like coal and natural gas. For powering vehicles, propane, especially renewable propane, has a lower carbon intensity than gasoline and diesel. By shifting towards energy with a lower CO2 intensity, we can significantly reduce the total greenhouse gas emissions contributing to global warming. Understanding the intensity scores of energy sources is particularly crucial when regulators and policymakers aim to reduce emissions in specific sectors, such as material handling or transportation. Rather than assuming electricity is always the best option, decision-makers can use these scores to choose solutions that truly minimize environmental impact, as evidenced by the ongoing debate in California regarding forklift regulations CARB’s Forklift Regulation.
It is essential for setting and achieving environmental targets.
Many countries and regions have committed to reducing their carbon footprint and transitioning to a low-carbon economy. Tracking the carbon intensity of their energy mix allows these entities to monitor progress towards these goals, identify areas for improvement, and adjust policies and strategies accordingly.
Understanding it also empowers consumers.
As awareness of environmental issues grows, more people are looking to reduce their personal impact on the planet. Knowledge of carbon intensity can guide consumers in making more sustainable choices, such as opting for propane-powered fleet vehicles over gasoline-powered cars or choosing energy providers that use a higher proportion of renewable energy.
Reducing CO2 intensity is vital for preserving our environment and health.
Lowering the reliance on high-carbon energy sources not only mitigates climate change but also reduces air pollution. This, in turn, has direct benefits for public health, contributing to fewer respiratory and cardiovascular diseases associated with poor air quality. The propane industry is actively working to lower its carbon intensity by investing in renewable propane production, which emits significantly fewer pollutants compared to conventional fuels. By increasing the availability of renewable propane, the industry aims to provide a sustainable and low-carbon alternative that meets energy needs while protecting the environment.
Understanding and reducing carbon intensity is a cornerstone of global efforts to tackle climate change, transition to sustainable energy, and protect human health and the environment. As we move forward, it will continue to be an essential consideration in shaping policies, guiding individual actions, and driving innovation in energy technologies.
Learn more about carbon emissions and green energy options in our previous blogs:
Turning the Tide on CO2 Emissions: The Path to Renewable Propane
Electrify Everything – Is That Really a Good Idea?
Additional Sources:
https://www.nationalgrid.com/stories/energy-explained/what-is-carbon-intensity
https://fortune.com/2021/06/25/carbon-intensity-emissions-climate-change-paris-agreement/
